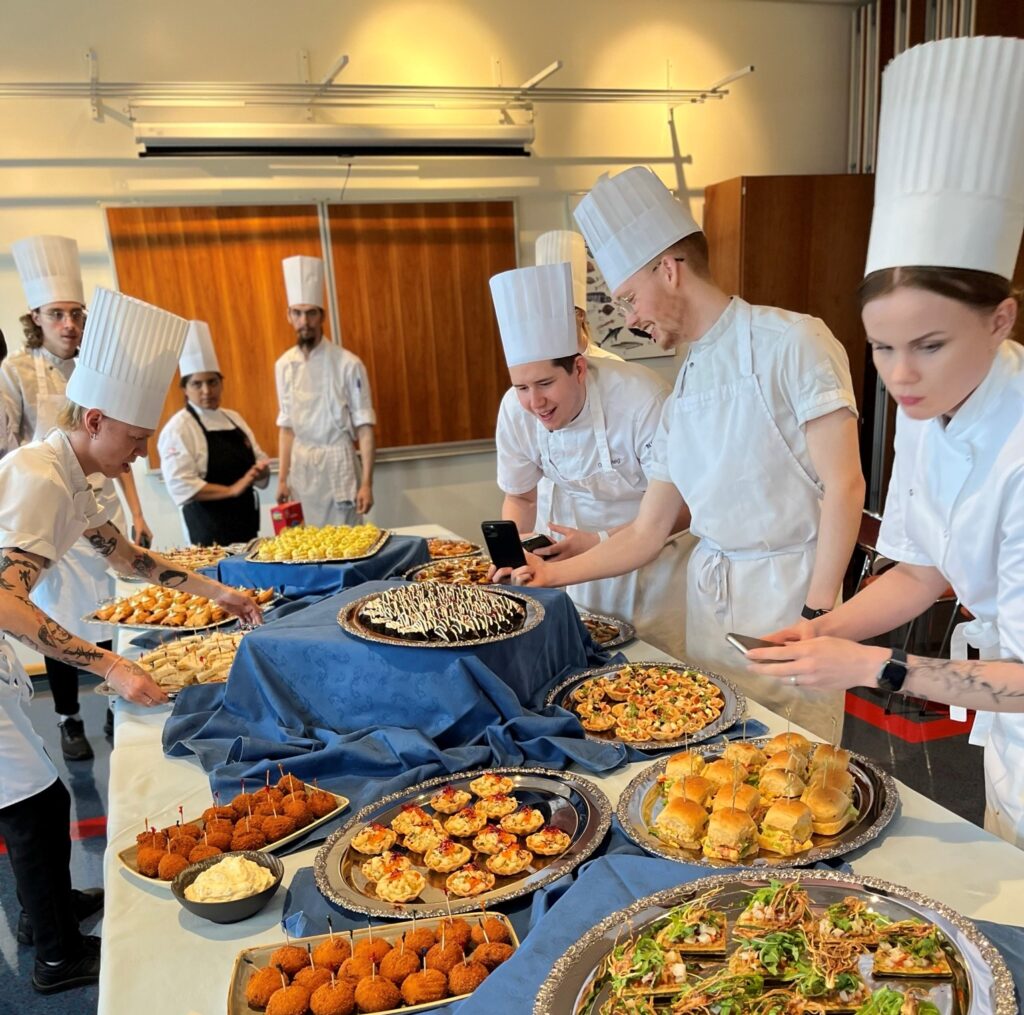
Vinnustofan „Af hverju saltfiskur?“ var haldin þann 28. september 2022. Markmið vinnustofunnar var að miðla þekkingu úr hinum ýmsu áttum, og leita leiða til að styrkja stöðu saltfisksins á innanlandsmarkaði. Vinnustofuna sóttu um 40 manns, matreiðslunemendur, matreiðslumeistarar, framleiðendur, markaðsfólk, og síðast en ekki síst Matvælaráðherra, Svandís Svavarsdóttir.

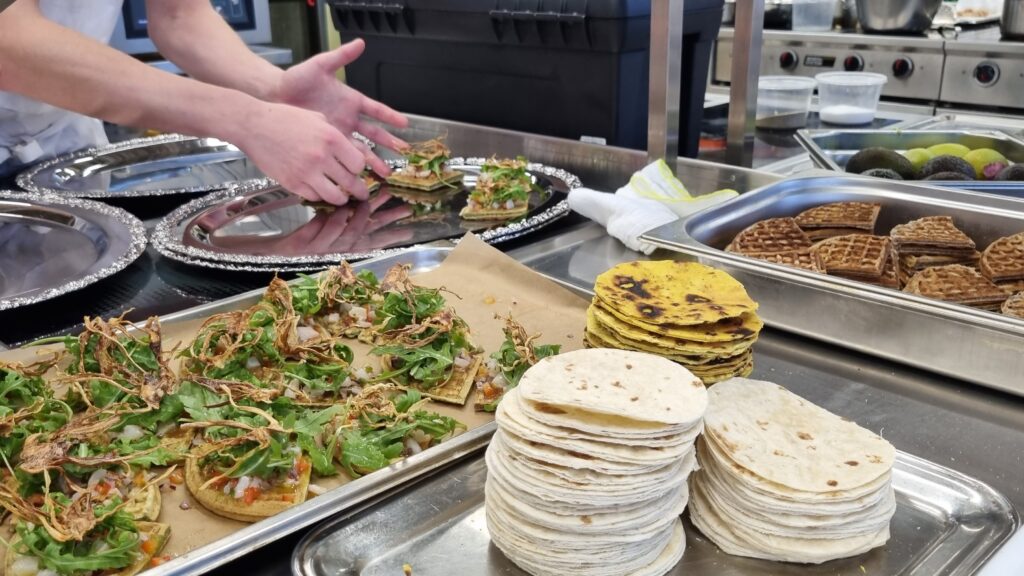
Haldnar voru stuttar kynningar af sérfræðingum Matís um sögu, menningu, verkun og útvötnun saltfisks. Jafnframt um þekkingu og viðhorf neytenda til saltfisks og neyslu hans á Íslandi. Skynrænir eiginleikar saltfisks voru kynntir og fundargestir fengu tækifæri til að smakka og bera saman tvær gerðir saltfisks og tvær gerðir af söltuðum fiski. Þá kynntu matreiðslunemar MK hugmyndir sínar á bakvið saltfiskrétti, sem voru reiddir á borð. Að því loknu var unnið í þremur hópum, sem hver um sig tók efirfarandi umræðuefni: “Hvað er saltfiskur- má kalla saltaðan fisk saltfisk?”, “Hvernig náum við til unga fólksins?” og “Hvernig er hægt að auka vöruframboðið?”
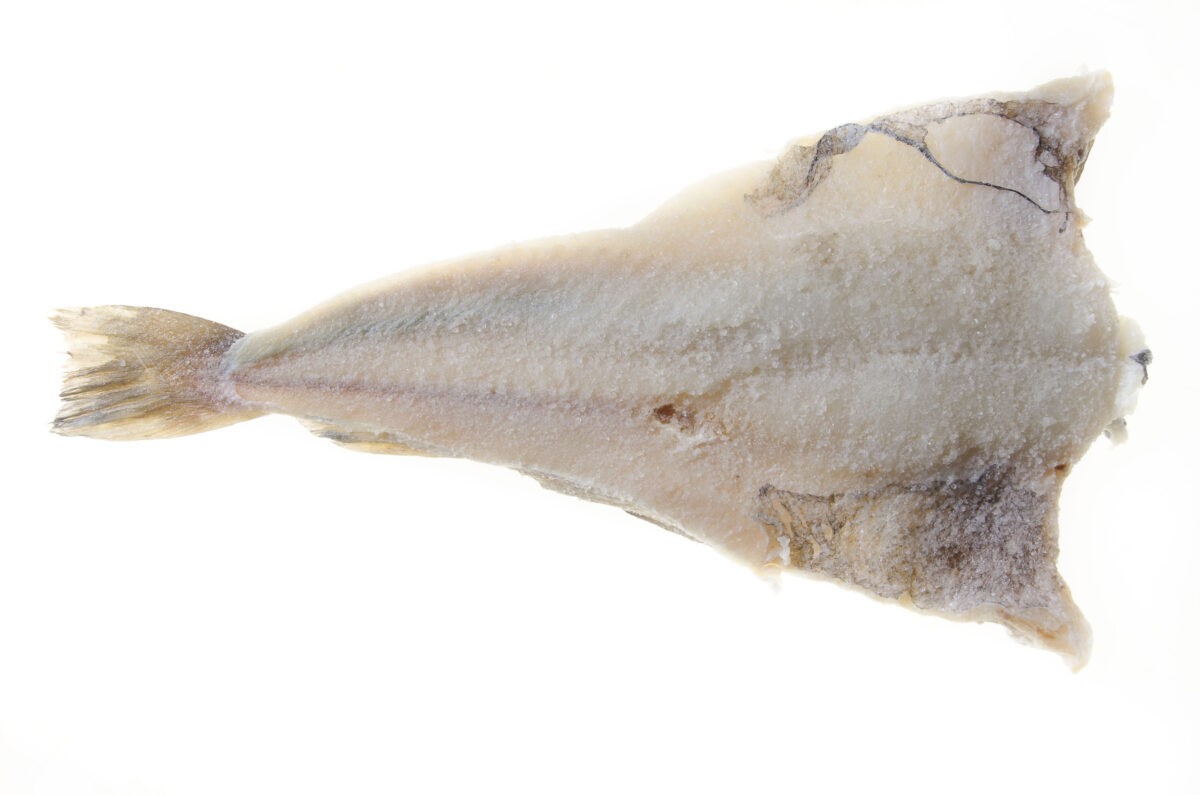
Niðurstöður vinnustofunnar sýndu að mikilvægt er að greina á milli þess sem sannarlega telst saltfiskur annars vegar og saltaðs fisks hins vegar. Saltaður fiskur, yfirleitt léttsaltaður eða nætursaltaður, hefur ekki sömu einkenni og saltfiskur, sem er fullverkaður með salti og saltpækli og þá þurrsaltaður jafnvel vikum saman, sem gefur þessari vöru einstaka eiginleika á borð við einkennandi verkunnarbragð og stinna áferð, eftir útvötnun.
Svo virðist sem það séu til staðar endalaus tækifæri og sóknarfæri fyrir saltfiskinn. Við þurfum hins vegar að greiða betur leið saltfisksins á íslenskan markað. Saltfiskur ætti í raun að vera okkur íslendingum, á pari við það sem parma skinka er Ítölum, hið minnsta.

Vinnustofan var haldin í húsakynnum Menntaskólans í Kópavogi, í samstarfi Matís, Gríms Kokks, Klúbbs Matreiðslumeistara, Menntaskólans í Kópavogi og Íslenskra saltfiskframleiðenda. Vinnustofan er hluti af verkefninu Saltfiskkræsingar (e. Trendy Cod) sem Matís hefur umsjón með, en NORA og AG-Fisk (Arbejdsgruppen for Fiskerisamarbejdet) á vegum Norrænu ráðherranefndarinnar hefur veitt styrk til.
Vinnslustöðin hf og KG Fiskverkun gáfu saltfisk til vinnustofunnar.

Kynntu þér verkefnið Saltfiskkræsingar nánar, með því að smella hnappinn hér að neðan:
Forsíðumynd af saltfisk: Lárus Karl Ingvarsson